Architecture¶
Faucet Design and Architecture¶
Faucet enables practical SDN for the masses (see http://queue.acm.org/detail.cfm?id=3015763).
- Drop in/replacement for non-SDN L2/L3 IPv4/IPv6 switch/router (easy migration)
- Packet forwarding/flooding/multicasting done entirely by switch hardware (controller only notified on topology change)
- BGP and static routing (other routing protocols provided by NFV)
- Multi vendor/platform support using OpenFlow 1.3 multi table
- Multi switch, vendor neutral “stacking” (Faucet distributed switching, loop free topology without spanning tree)
- ACLs, as well as allow/drop, allow packets to be copied/rewritten for external NFV applications
- Monitored with Prometheus
- Small code base with high code test coverage and automated testing both hardware and software
See unit and integration tests for working configuration examples.
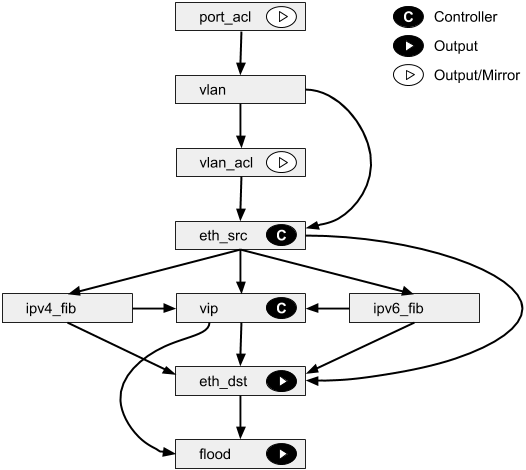
Faucet Openflow Switch Pipeline¶
This summarizes the global FAUCET pipeline; however, certain tables may be omitted if the functionality is not required. For example, if routing is not configured, neither FIB table nor the VIP table will be provisioned.
Usually the OpenFlow table IDs will be allocated sequentially for the tables actually used, so tables should be referenced by their name rather than the table ID in this diagram.
See also canonical pipeline definitions in faucet_pipeline.py.
PORT_ACL Table¶
- Apply user supplied ACLs to a port and send to next table
VLAN Table¶
- Match fields:
eth_dst, eth_type, in_port, vlan_vid - Operations:
- Drop unwanted L2 protocol traffic (and spoofing of Faucet’s virtual MAC)
- For tagged ports
- Match VLAN_VID and send to next table
- For untagged ports
- Push VLAN frame onto packet with VLAN_VID representing ports native VLAN and send to next table
- Interception of L2 control traffic (e.g. LACP, LLDP if configured).
- Unknown traffic is dropped
VLAN_ACL Table¶
- Apply user supplied ACLs to a VLAN and send to next table
ETH_SRC Table¶
- Match fields:
eth_dst, eth_src, eth_type, in_port, vlan_vid - Operations:
- For IPv4/IPv6 traffic where Faucet is the next hop, send to IPV4_FIB or IPV6_FIB (route)
- For known source MAC, send to ETH_DST (switch)
- For unknown source MACs, copy header to controller via packet in (for learning) and send to FLOOD
IPV4_FIB Table¶
- Match fields:
eth_type, ipv4_dst, vlan_vid - Operations:
- Route IPv4 traffic to a next-hop for each route we have learned
- Set eth_src to Faucet’s magic MAC address
- Set eth_dst to the resolved MAC address for the next-hop
- Decrement TTL
- Send to ETH_DST/HAIRPIN/VIP table
- Unknown traffic is dropped
IPV6_FIB Table¶
- Match fields:
eth_type, ipv6_dst, vlan_vid - Operations:
- Route IPv4 traffic to a next-hop for each route we have learned
- Set eth_src to Faucet’s magic MAC address
- Set eth_dst to the resolved MAC address for the next-hop
- Decrement TTL
- Send to ETH_DST/HAIRPIN/VIP table
- Unknown traffic is dropped
VIP Table¶
- Match fields:
arp_tpa, eth_dst, eth_type, icmpv6_type, ip_proto - Operations:
- Send traffic destined for FAUCET VIPs including IPv4 ARP and IPv6 ND to the controller, and traffic for unresolved hosts in connected IP subnets (if proactively learning).
- IPv4 ARP/IPv6 ND traffic may be flooded also (sent to FLOOD)
ETH_DST_HAIRPIN Table¶
- Exact match (no wildcards)
- Match fields:
eth_dst, in_port, vlan_vid - Operations:
- For destination MAC addresses we have learned output packet towards that host (popping VLAN frame if we are outputting on an untagged port), and where hairpinning is desired (e.g. routing between hosts on the same port, but different VLANS).
- Unknown traffic is sent to ETH_DST table.
ETH_DST Table¶
- Exaxct match (no wildcards)
- Match fields:
eth_dst, vlan_vid - Operations:
- For destination MAC addresses we have learned output packet towards that host (popping VLAN frame if we are outputting on an untagged port)
- Unknown traffic is sent to FLOOD table
FLOOD Table¶
- Match fields:
eth_dst, in_port, vlan_vid - Operations:
- Flood broadcast within VLAN
- Flood multicast within VLAN
- Unknown traffic is flooded within VLAN