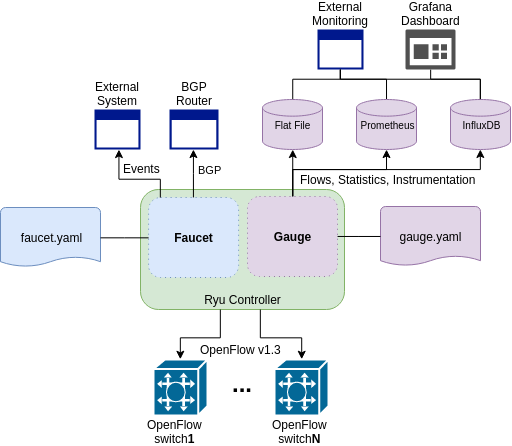
Architecture¶
Faucet Design and Architecture¶
Faucet enables practical SDN for the masses (see http://queue.acm.org/detail.cfm?id=3015763).
- Drop in/replacement for non-SDN L2/L3 IPv4/IPv6 switch/router (easy migration)
- Packet forwarding/flooding/multicasting done entirely by switch hardware (controller only notified on topology change)
- BGP and static routing (other routing protocols provided by NFV)
- Multi vendor/platform support using OpenFlow 1.3 multi table
- Multi switch, vendor neutral “stacking” (Faucet distributed switching, loop free topology without spanning tree)
- ACLs, as well as allow/drop, allow packets to be copied/rewritten for external NFV applications
- Monitored with Prometheus
- Small code base with high code test coverage and automated testing both hardware and software
See unit and integration tests for working configuration examples.
Faucet Openflow Switch Pipeline¶
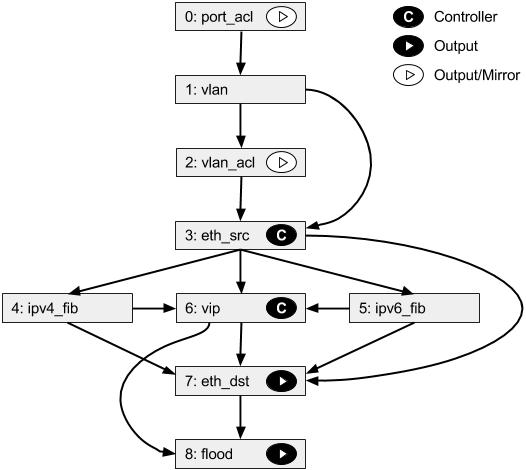
Table 0: PORT_ACL¶
- Apply user supplied ACLs to a port and send to next table
Table 1: VLAN¶
- Match fields:
eth_dst, eth_type, in_port, vlan_vid - Operations:
- Drop unwanted L2 protocol traffic (and spoofing of Faucet’s virtual MAC)
- For tagged ports
- Match VLAN_VID and send to next table
- For untagged ports
- Push VLAN frame onto packet with VLAN_VID representing ports native VLAN and send to next table
- Unknown traffic is dropped
Table 2: VLAN_ACL¶
- Apply user supplied ACLs to a VLAN and send to next table
Table 3: ETH_SRC¶
- Match fields:
eth_dst, eth_src, eth_type, in_port, vlan_vid - Operations:
- For IPv4/IPv6 traffic where Faucet is the next hop, send to IPV4_FIB or IPV6_FIB (route)
- For known source MAC, send to ETH_DST (switch)
- For unknown source MACs, copy header to controller via packet in (for learning) and send to FLOOD
Table 4: IPV4_FIB¶
- Match fields:
eth_type, ipv4_dst, vlan_vid - Operations:
- Route IPv4 traffic to a next-hop for each route we have learned
- Set eth_src to Faucet’s magic MAC address
- Set eth_dst to the resolved MAC address for the next-hop
- Decrement TTL
- Send to ETH_DST table
- Unknown traffic is dropped
Table 5: IPV6_FIB¶
- Match fields:
eth_type, ipv6_dst, vlan_vid - Operations:
- Route IPv4 traffic to a next-hop for each route we have learned
- Set eth_src to Faucet’s magic MAC address
- Set eth_dst to the resolved MAC address for the next-hop
- Decrement TTL
- Send to ETH_DST table
- Unknown traffic is dropped
Table 6: VIP¶
- Match fields:
arp_tpa, eth_dst, eth_type, icmpv6_type, ip_proto - Operations:
- Send traffic destined for FAUCET VIPs including IPv4 ARP and IPv6 ND to the controller.
- IPv6 ND traffic may be flooded also (sent to FLOOD)
Table 7: ETH_DST¶
- Match fields:
eth_dst, in_port, vlan_vid - Operations:
- For destination MAC addresses we have learned output packet towards that host (popping VLAN frame if we are outputting on an untagged port)
- Unknown traffic is sent to FLOOD table
Table 8: FLOOD¶
- Match fields:
eth_dst, in_port, vlan_vid - Operations:
- Flood broadcast within VLAN
- Flood multicast within VLAN
- Unknown traffic is flooded within VLAN
Faucet Architecture¶